Summary
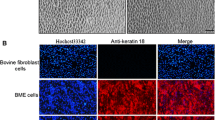
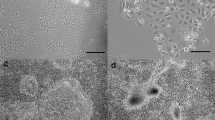
Elucidation of the bovine mammary gland's unique characteristics depends on obtaining an authentic cell line that will reproduce its function in vitro. Representative clones from bovine mammary cell populations, differing in their attachment capabilities, were cultured. L-1 cells showed strong attachment to the plate, whereas H-7 cells detached easily. Cultures established from these clones were nontumorigenic upon transplantation to an immunodeficient host; they exhibited the epithelial cell characteristics of positive cytokeratin but not smooth muscle actin staining. Both cell lines depended on fetal calf serum for proliferation. They exhibited distinct levels of differentiation on Matrigel in serum-free, insulin-supplemented medium on the basis of their organization and β-lactoglobulin (BLG) secretion. H-7 cells organized into mammospheres, whereas L-1 cells arrested in a duct-like morphology. In both cell lines, prolactin activated phosphorylation of the signal transducer and activator of transcription, Stat5—a regulator of milk protein gene transcription, and of PHAS-I—an inhibitor of translation initiation in its nonphosphorylated form. De novo synthesis and secretion of BLG were detected in differentiated cultures: in L-1 cells, BLG was dependent on lactogenic hormones for maximal induction but was less stringently controlled than was β-casein in the mouse CID-9 cell line. L-1 cells also encompassed a near-diploid chromosomal karyotype and may serve as a tool for studying functional characteristics of the bovine mammary gland.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ball, R. K.; Friis, R. R.; Schoenenberger, C. A., et al. Prolactin regulation of beta-casein gene expression and of a cytosolic 120-kd protein in a cloned mouse mammary epithelial cell line. EMBO J. 7:2089–2095; 1988.
Barash, I. Prolactin and insulin synergize to regulate the translation modulator PHAS-I via mitogen-activated protein kinase-independent but wortmannin- and rapamycin-sensitive pathway. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 155:37–49; 1999.
Barash, I.; Faerman, A.; Baruch, A., et al. Synthesis and secretion of human serum albumin by mammary gland explants of virgin and lactating transgenic mice. Transgenic Res. 2:266–276; 1993.
Baruch, A.; Shani, M.; Hourwitz, D., et al. Developmental regulation of the β-lactoglobulin/human serum albumin transgene is distinct from that of the β-lactoglobulin and endogenous β-casein gene in the mammary gland of transgenic mice. Dev. Genet. 16:241–252; 1995.
Danielson, K. G.; Oborn, C. J.; Durban, E. M., et al. Epithelial mouse mammary cell line exhibiting normal morphogenesis in vivo and functional differentiation in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:3756–3760; 1984.
Duchler, M. D.; Schmoll, F.; Pfneisl, F., et al. OMEC II: a new ovine mammary epithelial cell line. Biol. Cell 90:199–205; 1988.
Ebner, K. E.; Hageman, E. C.; Larson, B. L. Cultivation and properties of mammary cell cultures. Exp. Cell. Res. 23:373–385; 1961.
Gallie, D. R.; Traugh, J. A. Serum and insulin regulate cap function in 3T3-L1 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 269:7174–7179; 1994.
Groner, B.; Gouilleux, F. Prolactin-mediated gene activation in mammary epithelial cells. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 5:587–594; 1995.
Huynh, H. T.; Robitaille, G.; Turner, J. D. Establisment of bovine mammary epithelial cells (MAC-T): an in vitro model for bovine lactation. Exp. Cell Res. 197:191–199; 1991.
Ilan, I.; Barash, I.; Faerman, A., et al. Dual regulation of β-lactoglobulin/human serum albumin by the extracellular matrix in mammary cells from transgenic mice. Exp. Cell. Res. 224:28–38; 1996.
Ilan, N.; Barash, I.; Gootwine, E., et al. Establishment and initial characterization of the ovine mammary epithelial cell line NISH. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 34:326–332; 1998.
Kimball, S. R.; Jurasinski, C. V.; Lawrence, J. C., Jr., et al. Insulin stimulates protein synthesis in skeletal muscle by enhancing the association of eIF-4E and eIF-4C. Am. J. Physiol. 272:C754-C759; 1997.
Kordon, E. C.; Smith, G. H. An entire functional mammary gland may comprise the progeny from a single cell. Development 125:1921–1930; 1998.
Long, E.; Lazaris-Karatzas, A.; Karatzas, C., et al. Overexpressing eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E stimulates bovine mammary epithelial cell population. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 33:133–141; 2001.
MacKenzie, D. D.; Forsyth, I. A.; Brooker, B. E., et al. Culture of bovine mammary epithelial cells on collagen gels. Tissue Cell 14:231–241; 1982.
Merrick, W. C.; Hershey, J. W. B. The pathway and mechanism of eukaryotic protein synthesis. In: Hershey, J. W. B.; Mathews, M. B.; Sonenberg, N., ed. Translation control. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1996:31–69.
Pechoux, C.; Gudjonsson, T.; Ronnov-Jessen, L., et al. Human mammary luminal epithelial cells contain progenitors to myoepithelial cells. Dev. Biol. 206:88–99; 1999.
Piedrahita, J. A. Targeted modification of the domestic animal genome. Theriogenology 53:105–116; 2000.
Ramagnolo, D.; Akers, R. M.; Byatt, J. C., et al. IGF-I-induced IGFBP-3 potentiates the mitogenic actions of IGF-I in mammary epithelial MD-IGF-I cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 102:131–139; 1994.
Robinson, R. M.; Akers, R. M.; Forsten, K. E. Real-time detection of insulin-like growth factor-1 stimulation of the MAC-T bovine mammary epithelial cell line. Endocrine 13:345–352; 2000a.
Robinson, R. M.; Akers, R. M.; Forsten, K. E. Microphysiometry to evaluate real-time response of mammary epithelial cells to IGF-I. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 28:209–211; 2000b.
Romagnolo, D.; Akers, R. M.; Wong, E. A., et al. Lactogenic hormones and extracellular matrix regulate expression of IGF-1 linked to MMTV-LTR in mammary epithelial cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 96:147–157; 1993.
Rosen, J. M.; Wyszomierski, S. L.; Hadsell, D. Regulation of milk protein gene expression. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 19:407–436; 1999.
Schmidhauser C.; Bissell, M. J.; Myers, C., et al. Extracellular matrix and hormones transcriptionally regulate bovine β-casein 5′ sequences in stably transfected mouse mammary cells. proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:9118–9122; 1990.
Wheeler, T. T.; Broadhurst, M. K.; Sadowski, H. B., et al. Stat5 phosphorylation status and DNA-binding activity in the bovine and murine mammary glands. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 176:39–48; 2001.
Wheeler, T. T.; Kuys, Y. M.; Broadhurst, M. M., et al. Mammary Stat5 abundance and activity are not altered with lactation state in cows. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 133:141–149; 1997.
Wilde, C. J.; Knight, C. H.; Flint, D. J. Control of milk secretion and apoptosis during mammary involution. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 4:129–136; 1999.
Woodward, T. L.; Turner, J. D.; Hung, H. T., et al. Inhibition of cellular proliferation and modulation of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins by retinoids in a bovine mammary epithelial cell line. J. Cell. Physiol. 167:488–499; 1996.
Yang, J.; Kennelly, J. J.; Baracos, V. E. Physiological levels of Stat5 DNA binding activity and protein in bovine mammary gland. J. Anim. Sci. 78:3126–3134; 2000a.
Yang, J.; Kennelly, J. J.; Baracos, V. E. The activity of transcription factor Stat5 responds to prolactin, growth hormone, and IGF-I in rat and bovine mammary explant culture. J. Anim. Sci. 78:3114–3125; 2000b.
Zavizion, B.; van Duffelen, M.; Schaeffer, W., et al. Establishment and characterization of a bovine mammary myoepithelial cell line. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 32:149–158; 1996.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
German, T., Barash, I. Characterization of an epithelial cell line from bovine mammary gland. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 38, 282–292 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1290/1071-2690(2002)038<0282:COAECL>2.0.CO;2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1290/1071-2690(2002)038<0282:COAECL>2.0.CO;2